On this page
1. Spring 批处理集成
1.1. Spring Batch 集成介绍
Spring Batch 的许多用户可能会遇到超出 Spring Batch 范围的要求,但可以通过使用 Spring Integration 来高效,简洁地实现这些要求。相反,Spring Integration 用户可能会遇到 Spring Batch 要求,并需要一种有效地集成两个框架的方法。在这种情况下,出现了几种模式和用例,Spring Batch Integration 解决了这些需求。
Spring Batch 和 Spring Integration 之间的界线并不总是很清楚,但是有两个建议可以帮助您:考虑粒度,并应用通用模式。这些常见模式中的一些在本参考手册部分中进行了描述。
将消息添加到批处理过程中,可以实现自动化操作以及关键问题的分离和制定策略。例如,一条消息可能触发作业执行,然后可以通过多种方式公开消息的发送。或者,当作业完成或失败时,该事件可能会触发消息发送,并且这些消息的使用者可能会遇到与应用程序本身无关的操作问题。消息传递也可以嵌入到作业中(例如,通过通道读取或写入要处理的 Item)。远程分区和远程分块提供了在多个工作人员上分配工作负载的方法。
本节涵盖以下关键概念:
1.1.1. 命名空间支持
从 Spring Batch Integration 1.3 开始,添加了专用的 XML 命名空间支持,目的是提供更轻松的配置体验。为了激活名称空间,请将以下名称空间声明添加到您的 Spring XML Application Context 文件中:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:batch-int="http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch-integration"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch-integration
https://www.springframework.org/schema/batch-integration/spring-batch-integration.xsd">
...
</beans>
完整配置的用于 Spring Batch Integration 的 Spring XML Application Context 文件可能如下所示:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:int="http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration"
xmlns:batch="http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch"
xmlns:batch-int="http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch-integration"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch-integration
https://www.springframework.org/schema/batch-integration/spring-batch-integration.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch
https://www.springframework.org/schema/batch/spring-batch.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration
https://www.springframework.org/schema/integration/spring-integration.xsd">
...
</beans>
也允许将版本号附加到引用的 XSD 文件中,但是,由于无版本声明始终使用最新的架构,因此我们通常不建议将版本号附加到 XSD 名称中。在更新 Spring Batch Integration 依赖项时,添加版本号可能会产生问题,因为它们可能需要 XML 模式的最新版本。
1.1.2. 通过消息启动批处理作业
使用核心 Spring Batch API 启动批处理作业时,基本上有 2 个选项:
在命令行中使用
CommandLineJobRunner以编程方式,使用
JobOperator.start()或JobLauncher.run()
例如,当您使用 Shell 脚本调用批处理作业时,可能要使用CommandLineJobRunner。另外,您也可以直接使用JobOperator(例如,在将 Spring Batch 用作 Web 应用程序的一部分时)。但是,更复杂的用例呢?也许您需要轮询远程(S)FTP 服务器以检索批处理作业的数据,或者您的应用程序必须同时支持多个不同的数据源。例如,您不仅可以从 Web 接收数据文件,还可以从 FTP 和其他来源接收数据文件。也许在调用 Spring Batch 之前需要对 Importing 文件进行其他转换。
因此,使用 Spring Integration 及其众多适配器来执行批处理作业将更加强大。例如,您可以使用文件入站通道适配器监视文件系统中的目录,并在 Importing 文件到达后立即启动批处理作业。另外,您可以创建使用多个不同适配器的 Spring Integration 流,仅使用配置即可轻松地同时从多个源中获取批处理作业的数据。通过 Spring Integration 轻松实现所有这些场景,因为它允许对事件JobLauncher进行解耦,事件驱动的执行。
Spring Batch Integration 提供了JobLaunchingMessageHandler类,可用于启动批处理作业。 JobLaunchingMessageHandler的 Importing 由 Spring Integration 消息提供,其有效负载类型为JobLaunchRequest。此类是围绕需要启动的Job和启动批处理作业所必需的JobParameters的包装。
下图说明了用于启动批处理作业的典型 Spring Integration 消息流。 EIP(企业集成模式)网站提供了消息图标及其描述的完整概述。
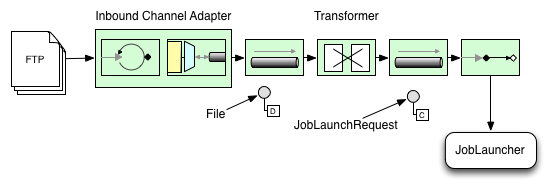
图 1.启动批处理作业
将文件转换为 JobLaunchRequest
package io.spring.sbi;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Job;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobParametersBuilder;
import org.springframework.batch.integration.launch.JobLaunchRequest;
import org.springframework.integration.annotation.Transformer;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
import java.io.File;
public class FileMessageToJobRequest {
private Job job;
private String fileParameterName;
public void setFileParameterName(String fileParameterName) {
this.fileParameterName = fileParameterName;
}
public void setJob(Job job) {
this.job = job;
}
@Transformer
public JobLaunchRequest toRequest(Message<File> message) {
JobParametersBuilder jobParametersBuilder =
new JobParametersBuilder();
jobParametersBuilder.addString(fileParameterName,
message.getPayload().getAbsolutePath());
return new JobLaunchRequest(job, jobParametersBuilder.toJobParameters());
}
}
JobExecution 响应
执行批处理作业时,将返回JobExecution实例。该实例可用于确定执行状态。如果能够成功创建JobExecution,则无论实际执行是否成功,都将始终返回它。
如何返回JobExecution实例的确切行为取决于所提供的TaskExecutor。如果使用synchronous(单线程)TaskExecutor实现,则仅after作业完成时返回JobExecution响应。使用asynchronous TaskExecutor时,会立即返回JobExecution实例。然后,用户可以使用JobExecution实例的id(使用JobExecution.getJobId()),并使用JobExplorer向JobRepository查询作业的更新状态。有关更多信息,请参阅查询存储库上的 Spring Batch 参考文档。
Spring Batch 集成配置
以下配置将在提供的目录中创建文件inbound-channel-adapter来侦听 CSV 文件,将其交给我们的转换器(FileMessageToJobRequest),通过* Job Launching Gateway *启动作业,然后使用logging-channel-adapter记录JobExecution的输出。
XML Configuration
<int:channel id="inboundFileChannel"/>
<int:channel id="outboundJobRequestChannel"/>
<int:channel id="jobLaunchReplyChannel"/>
<int-file:inbound-channel-adapter id="filePoller"
channel="inboundFileChannel"
directory="file:/tmp/myfiles/"
filename-pattern="*.csv">
<int:poller fixed-rate="1000"/>
</int-file:inbound-channel-adapter>
<int:transformer input-channel="inboundFileChannel"
output-channel="outboundJobRequestChannel">
<bean class="io.spring.sbi.FileMessageToJobRequest">
<property name="job" ref="personJob"/>
<property name="fileParameterName" value="input.file.name"/>
</bean>
</int:transformer>
<batch-int:job-launching-gateway request-channel="outboundJobRequestChannel"
reply-channel="jobLaunchReplyChannel"/>
<int:logging-channel-adapter channel="jobLaunchReplyChannel"/>
Java Configuration
@Bean
public FileMessageToJobRequest fileMessageToJobRequest() {
FileMessageToJobRequest fileMessageToJobRequest = new FileMessageToJobRequest();
fileMessageToJobRequest.setFileParameterName("input.file.name");
fileMessageToJobRequest.setJob(personJob());
return fileMessageToJobRequest;
}
@Bean
public JobLaunchingGateway jobLaunchingGateway() {
SimpleJobLauncher simpleJobLauncher = new SimpleJobLauncher();
simpleJobLauncher.setJobRepository(jobRepository);
simpleJobLauncher.setTaskExecutor(new SyncTaskExecutor());
JobLaunchingGateway jobLaunchingGateway = new JobLaunchingGateway(simpleJobLauncher);
return jobLaunchingGateway;
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow integrationFlow(JobLaunchingGateway jobLaunchingGateway) {
return IntegrationFlows.from(Files.inboundAdapter(new File("/tmp/myfiles")).
filter(new SimplePatternFileListFilter("*.csv")),
c -> c.poller(Pollers.fixedRate(1000).maxMessagesPerPoll(1))).
handle(fileMessageToJobRequest()).
handle(jobLaunchingGateway).
log(LoggingHandler.Level.WARN, "headers.id + ': ' + payload").
get();
}
ItemReader 配置示例
现在我们正在轮询文件并启动作业,我们需要配置我们的 Spring Batch ItemReader(例如)以使用在名为“ input.file.name”的作业参数定义的位置找到的文件,如下所示 bean 配置:
XML Configuration
<bean id="itemReader" class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.FlatFileItemReader"
scope="step">
<property name="resource" value="file://#{jobParameters['input.file.name']}"/>
...
</bean>
Java Configuration
@Bean
@StepScope
public ItemReader sampleReader(@Value("#{jobParameters[input.file.name]}") String resource) {
...
FlatFileItemReader flatFileItemReader = new FlatFileItemReader();
flatFileItemReader.setResource(new FileSystemResource(resource));
...
return flatFileItemReader;
}
前面示例中的主要关注点是将#{jobParameters['input.file.name']}的值注入为 Resource 属性值,并将ItemReader bean 设置为具有* Step scope *。将 bean 设置为具有 Step 作用域将利用后期绑定支持的优势,该支持允许访问jobParameters变量。
1.2. 作业启动网关的可用属性
作业启动网关具有以下属性,您可以设置这些属性来控制作业:
id:标识基础 Spring bean 定义,该定义是以下任一个的实例:EventDrivenConsumerPollingConsumer(确切的实现取决于组件的 Importing 通道是SubscribableChannel还是PollableChannel.)
auto-startup:布尔值标志,指示端点应在启动时自动启动。默认值为* true *。request-channel:此端点的 ImportingMessageChannel。最终的
JobExecution有效负载发送到的reply-channel:MessageChannel。reply-timeout:允许您指定此网关在引发异常之前 await 成功将回复消息发送到回复通道的时间(以毫秒为单位)。仅当通道可能阻塞时(例如,使用当前已满的有界队列通道时),此属性才适用。另外,请记住,当发送到DirectChannel时,调用发生在发送者的线程中。因此,发送操作的失败可能是由更下游的其他组件引起的。reply-timeout属性 Map 到基础MessagingTemplate实例的sendTimeout属性。如果未指定,则属性默认为 -1 </ emphasis>,这意味着,默认情况下Gateway无限期 await。job-launcher:可选。接受自定义JobLauncherbean 引用。如果未指定,适配器将重新使用在jobLauncher的id下注册的实例。如果不存在默认实例,则将引发异常。order:指定此端点作为订户连接到SubscribableChannel时的调用 Sequences。
1.3. Sub-Elements
当此Gateway从PollableChannel接收消息时,您必须提供全局默认值Poller或为Job Launching Gateway提供Poller子元素,如以下示例所示:
XML Configuration
<batch-int:job-launching-gateway request-channel="queueChannel"
reply-channel="replyChannel" job-launcher="jobLauncher">
<int:poller fixed-rate="1000">
</batch-int:job-launching-gateway>
Java Configuration
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "queueChannel", poller = @Poller(fixedRate="1000"))
public JobLaunchingGateway sampleJobLaunchingGateway() {
JobLaunchingGateway jobLaunchingGateway = new JobLaunchingGateway(jobLauncher());
jobLaunchingGateway.setOutputChannel(replyChannel());
return jobLaunchingGateway;
}
1.3.1. 提供信息性消息的反馈
由于 Spring Batch 作业可以长期运行,因此提供进度信息通常很关键。例如,如果批处理作业的某些或全部部分失败,则可能希望通知利益相关者。 Spring Batch 支持通过以下方式收集此信息:
Active polling
Event-driven listeners
异步启动 Spring Batch 作业时(例如,使用Job Launching Gateway),将返回JobExecution实例。因此,通过使用JobExplorer从JobRepository检索JobExecution的更新实例,可以使用JobExecution.getJobId()连续轮询状态更新。但是,这被认为是次优的,因此应首选事件驱动的方法。
因此,Spring Batch 提供了侦听器,包括三个最常用的侦听器:
StepListener
ChunkListener
JobExecutionListener
在下图所示的示例中,已使用StepExecutionListener配置了 Spring Batch 作业。因此,Spring Integration 接收并处理事件之前或之后的任何步骤。例如,可以使用Router检查接收到的StepExecution。根据检查的结果,可能会发生各种事情(例如,将消息路由到邮件出站通道适配器),以便可以根据某种条件发送电子邮件通知。
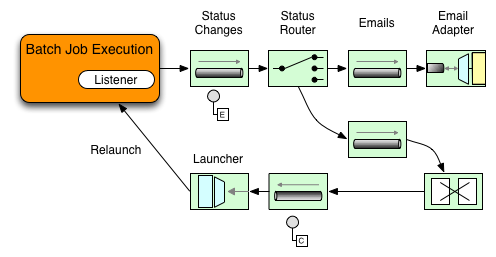
图 2.处理信息性消息
下面的两部分示例显示了侦听器如何配置为针对StepExecution事件向Gateway发送消息并将其输出记录到logging-channel-adapter。
首先,创建通知集成 Bean:
XML Configuration
<int:channel id="stepExecutionsChannel"/>
<int:gateway id="notificationExecutionsListener"
service-interface="org.springframework.batch.core.StepExecutionListener"
default-request-channel="stepExecutionsChannel"/>
<int:logging-channel-adapter channel="stepExecutionsChannel"/>
Java Configuration
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "stepExecutionsChannel")
public LoggingHandler loggingHandler() {
LoggingHandler adapter = new LoggingHandler(LoggingHandler.Level.WARN);
adapter.setLoggerName("TEST_LOGGER");
adapter.setLogExpressionString("headers.id + ': ' + payload");
return adapter;
}
@MessagingGateway(name = "notificationExecutionsListener", defaultRequestChannel = "stepExecutionsChannel")
public interface NotificationExecutionListener extends StepExecutionListener {}
Note
您将需要在配置中添加@IntegrationComponentScanComments。
其次,修改您的工作以添加步骤级别的侦听器:
XML Configuration
<job id="importPayments">
<step id="step1">
<tasklet ../>
<chunk ../>
<listeners>
<listener ref="notificationExecutionsListener"/>
</listeners>
</tasklet>
...
</step>
</job>
Java Configuration
public Job importPaymentsJob() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("importPayments")
.start(stepBuilderFactory.get("step1")
.chunk(200)
.listener(notificationExecutionsListener())
...
}
1.3.2. 异步处理器
异步处理器可帮助您扩展 Item 的处理。在异步处理器用例中,AsyncItemProcessor充当调度程序,对新线程上的 Item 执行ItemProcessor的逻辑。Item 完成后,Future将传递到AsynchItemWriter进行写入。
因此,您可以使用异步 Item 处理来提高性能,基本上可以实现* fork-join *方案。 AsyncItemWriter收集结果并在所有结果可用后立即写回该块。
以下示例显示了如何配置AsyncItemProcessor:
XML Configuration
<bean id="processor"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.async.AsyncItemProcessor">
<property name="delegate">
<bean class="your.ItemProcessor"/>
</property>
<property name="taskExecutor">
<bean class="org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor"/>
</property>
</bean>
Java Configuration
@Bean
public AsyncItemProcessor processor(ItemProcessor itemProcessor, TaskExecutor taskExecutor) {
AsyncItemProcessor asyncItemProcessor = new AsyncItemProcessor();
asyncItemProcessor.setTaskExecutor(taskExecutor);
asyncItemProcessor.setDelegate(itemProcessor);
return asyncItemProcessor;
}
delegate属性引用您的ItemProcessor bean,而taskExecutor属性引用您选择的TaskExecutor。
以下示例显示了如何配置AsyncItemWriter:
XML Configuration
<bean id="itemWriter"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.async.AsyncItemWriter">
<property name="delegate">
<bean id="itemWriter" class="your.ItemWriter"/>
</property>
</bean>
Java Configuration
@Bean
public AsyncItemWriter writer(ItemWriter itemWriter) {
AsyncItemWriter asyncItemWriter = new AsyncItemWriter();
asyncItemWriter.setDelegate(itemWriter);
return asyncItemWriter;
}
同样,delegate属性实际上是对ItemWriter bean 的引用。
1.3.3. 外化批处理执行
到目前为止讨论的集成方法建议使用案例,其中 Spring Integration 像 Shell 一样包装 Spring Batch。但是,Spring Batch 也可以在内部使用 Spring Integration。使用这种方法,Spring Batch 用户可以将 Item 甚至块的处理委派给外部流程。这使您可以卸载复杂的处理。 Spring Batch Integration 为以下方面提供了专门的支持:
Remote Chunking
Remote Partitioning
Remote Chunking
图 3.远程分块
更进一步,人们还可以使用ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter(由 Spring Batch Integration 提供)将块处理外部化,后者发送 Item 并收集结果。发送后,Spring Batch continue 读取和分组 Item 的过程,而无需 await 结果。相反,ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter负责收集结果并将其重新集成到 Spring Batch 流程中。
使用 Spring Integration,您可以完全控制进程的并发性(例如,使用QueueChannel而不是DirectChannel)。此外,通过依赖 Spring Integration 丰富的通道适配器(例如 JMS 和 AMQP)集合,您可以将 Batch 作业的块分发到外部系统进行处理。
一个具有要远程分块的步骤的简单作业,其配置可能类似于以下内容:
XML Configuration
<job id="personJob">
<step id="step1">
<tasklet>
<chunk reader="itemReader" writer="itemWriter" commit-interval="200"/>
</tasklet>
...
</step>
</job>
Java Configuration
public Job chunkJob() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("personJob")
.start(stepBuilderFactory.get("step1")
.<Person, Person>chunk(200)
.reader(itemReader())
.writer(itemWriter())
.build())
.build();
}
ItemReader参考指向您要用于在主服务器上读取数据的 bean。如上所述,ItemWriter参考指向特殊的ItemWriter(称为ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter)。处理器(如果有)保留在主服务器上,因为它是在工作服务器上配置的。以下配置提供了基本的主设置。在实现用例时,应检查所有其他组件属性,例如节流阀限制等。
XML Configuration
<bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory">
<property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616"/>
</bean>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter id="jmsRequests" destination-name="requests"/>
<bean id="messagingTemplate"
class="org.springframework.integration.core.MessagingTemplate">
<property name="defaultChannel" ref="requests"/>
<property name="receiveTimeout" value="2000"/>
</bean>
<bean id="itemWriter"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.chunk.ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter"
scope="step">
<property name="messagingOperations" ref="messagingTemplate"/>
<property name="replyChannel" ref="replies"/>
</bean>
<int:channel id="replies">
<int:queue/>
</int:channel>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter id="jmsReplies"
destination-name="replies"
channel="replies"/>
Java Configuration
@Bean
public org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
ActiveMQConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory();
factory.setBrokerURL("tcp://localhost:61616");
return factory;
}
/*
* Configure outbound flow (requests going to workers)
*/
@Bean
public DirectChannel requests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(requests())
.handle(Jms.outboundAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("requests"))
.get();
}
/*
* Configure inbound flow (replies coming from workers)
*/
@Bean
public QueueChannel replies() {
return new QueueChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow inboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("replies"))
.channel(replies())
.get();
}
/*
* Configure the ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter
*/
@Bean
public ItemWriter<Integer> itemWriter() {
MessagingTemplate messagingTemplate = new MessagingTemplate();
messagingTemplate.setDefaultChannel(requests());
messagingTemplate.setReceiveTimeout(2000);
ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter<Integer> chunkMessageChannelItemWriter
= new ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter<>();
chunkMessageChannelItemWriter.setMessagingOperations(messagingTemplate);
chunkMessageChannelItemWriter.setReplyChannel(replies());
return chunkMessageChannelItemWriter;
}
前面的配置为我们提供了许多 bean。我们使用 ActiveMQ 和 Spring Integration 提供的入站/出站 JMS 适配器配置消息传递中间件。如图所示,工作步骤引用的itemWriter bean 使用ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter在已配置的中间件上写入块。
现在,我们可以 continue 进行工作程序配置,如以下示例所示:
XML Configuration
<bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory">
<property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616"/>
</bean>
<int:channel id="requests"/>
<int:channel id="replies"/>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter id="incomingRequests"
destination-name="requests"
channel="requests"/>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter id="outgoingReplies"
destination-name="replies"
channel="replies">
</int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter>
<int:service-activator id="serviceActivator"
input-channel="requests"
output-channel="replies"
ref="chunkProcessorChunkHandler"
method="handleChunk"/>
<bean id="chunkProcessorChunkHandler"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.chunk.ChunkProcessorChunkHandler">
<property name="chunkProcessor">
<bean class="org.springframework.batch.core.step.item.SimpleChunkProcessor">
<property name="itemWriter">
<bean class="io.spring.sbi.PersonItemWriter"/>
</property>
<property name="itemProcessor">
<bean class="io.spring.sbi.PersonItemProcessor"/>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
Java Configuration
@Bean
public org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
ActiveMQConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory();
factory.setBrokerURL("tcp://localhost:61616");
return factory;
}
/*
* Configure inbound flow (requests coming from the master)
*/
@Bean
public DirectChannel requests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow inboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("requests"))
.channel(requests())
.get();
}
/*
* Configure outbound flow (replies going to the master)
*/
@Bean
public DirectChannel replies() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(replies())
.handle(Jms.outboundAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("replies"))
.get();
}
/*
* Configure the ChunkProcessorChunkHandler
*/
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "requests", outputChannel = "replies")
public ChunkProcessorChunkHandler<Integer> chunkProcessorChunkHandler() {
ChunkProcessor<Integer> chunkProcessor
= new SimpleChunkProcessor<>(itemProcessor(), itemWriter());
ChunkProcessorChunkHandler<Integer> chunkProcessorChunkHandler
= new ChunkProcessorChunkHandler<>();
chunkProcessorChunkHandler.setChunkProcessor(chunkProcessor);
return chunkProcessorChunkHandler;
}
这些配置项中的大多数应该从主配置中 Watch 起来很熟悉。Worker 不需要访问 Spring Batch JobRepository或实际的作业配置文件。感兴趣的主要 bean 是chunkProcessorChunkHandler。 ChunkProcessorChunkHandler的chunkProcessor属性采用已配置的SimpleChunkProcessor,在该位置您将提供对ItemWriter(以及(可选)ItemProcessor)的引用,该引用将在工作线程从主服务器接收到块时在工作线程上运行。
有关更多信息,请参见Remote Chunking的“可伸缩性”一章中的部分。
从 4.1 版本开始,Spring Batch Integration 引入了@EnableBatchIntegration注解,该注解可用于简化远程分块设置。此注解提供了两个可以在应用程序上下文中自动装配的 bean:
RemoteChunkingMasterStepBuilderFactory:用于配置主步骤RemoteChunkingWorkerBuilder:用于配置远程工 Writer 集成流程
这些 API 负责配置许多组件,如下图所示:
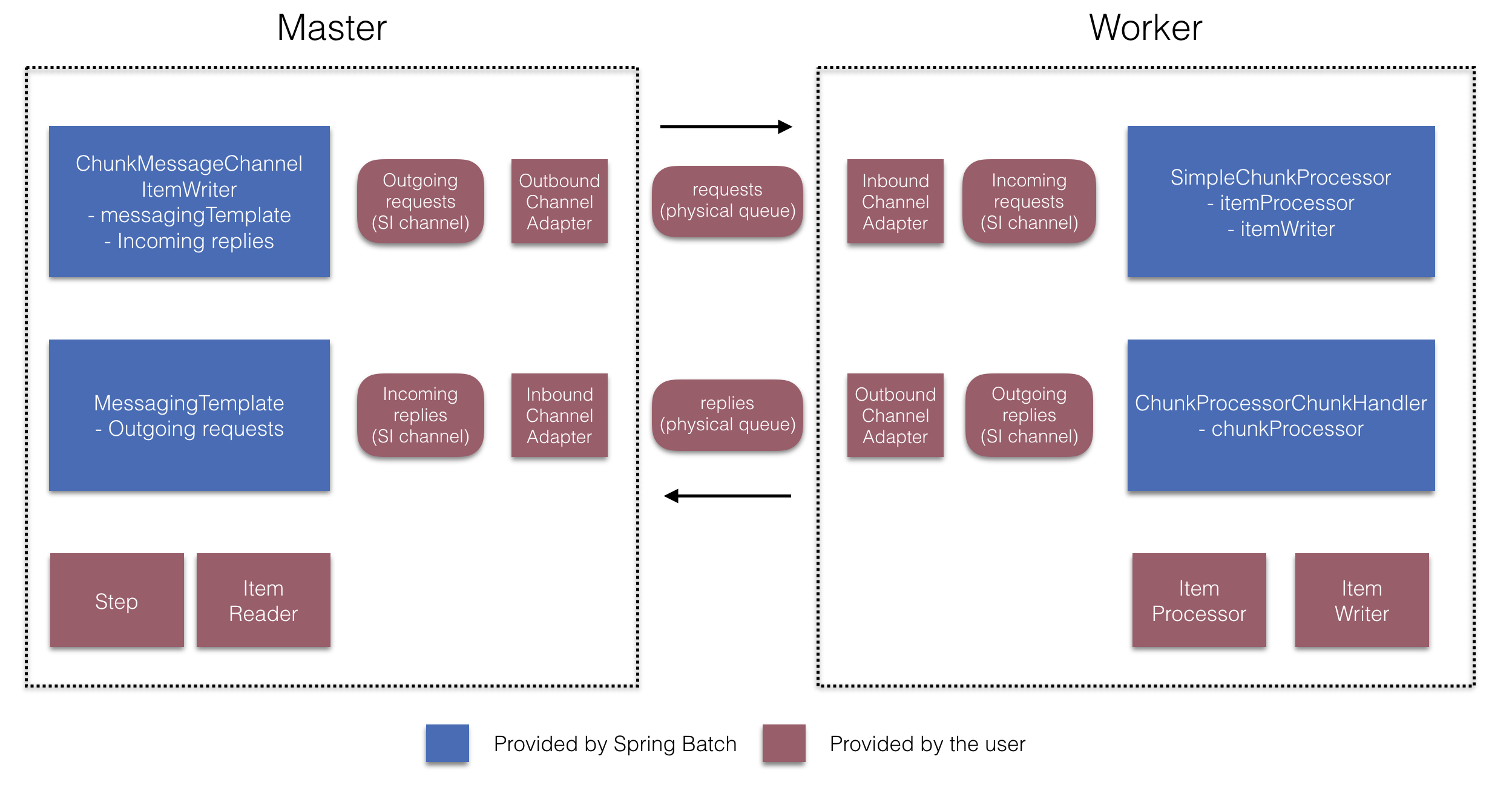
图 4.远程分块配置
在主服务器端,RemoteChunkingMasterStepBuilderFactory允许您pass 语句以下内容来配置主服务器步骤:
itemReader 读取 item 并将其发送给 Worker
输出通道(“传出请求”)将请求发送给工作人员
Importing 通道(“传入答复”)以接收工作人员的答复
不需要显式配置ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter和MessagingTemplate(如果需要,仍可以显式配置它们)。
在工作程序端,RemoteChunkingWorkerBuilder允许您将工作程序配置为:
侦听主机在 Importing 通道上发送的请求(“传入请求”)
使用已配置的
ItemProcessor和ItemWriter为每个请求调用ChunkProcessorChunkHandler的handleChunk方法将输出通道上的回复(“传出回复”)发送给主服务器
无需显式配置SimpleChunkProcessor和ChunkProcessorChunkHandler(可以根据需要显式配置它们)。
以下示例显示了如何使用这些 API:
@EnableBatchIntegration
@EnableBatchProcessing
public class RemoteChunkingJobConfiguration {
@Configuration
public static class MasterConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemoteChunkingMasterStepBuilderFactory masterStepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public TaskletStep masterStep() {
return this.masterStepBuilderFactory.get("masterStep")
.chunk(100)
.reader(itemReader())
.outputChannel(requests()) // requests sent to workers
.inputChannel(replies()) // replies received from workers
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
@Configuration
public static class WorkerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemoteChunkingWorkerBuilder workerBuilder;
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow workerFlow() {
return this.workerBuilder
.itemProcessor(itemProcessor())
.itemWriter(itemWriter())
.inputChannel(requests()) // requests received from the master
.outputChannel(replies()) // replies sent to the master
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
}
您可以找到远程分块作业here的完整示例。
Remote Partitioning
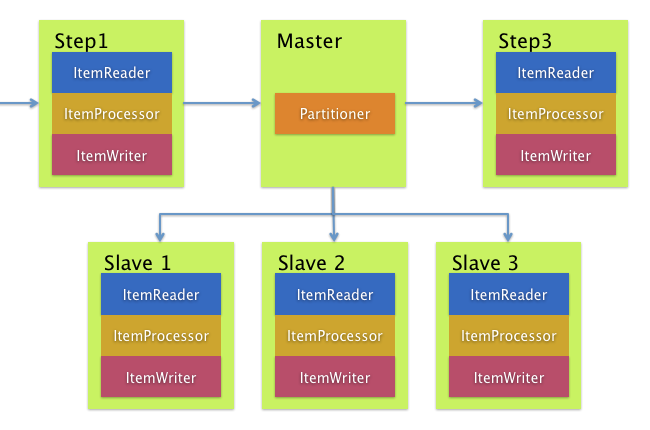
图 5.远程分区
另一方面,如果不是分区处理而是导致瓶颈的相关 I/O,则远程分区很有用。使用远程分区,可以将工作分配给执行完整 Spring Batch 步骤的工作人员。因此,每个 Worker 都有自己的ItemReader,ItemProcessor和ItemWriter。为此,Spring Batch Integration 提供了MessageChannelPartitionHandler。
PartitionHandler接口的此实现使用MessageChannel实例向远程工作程序发送指令并接收其响应。这提供了用于与远程工 Writer 通信的传输(例如 JMS 和 AMQP)的很好的抽象。
“可伸缩性”一章的第remote partitioning部分提供了配置远程分区所需的概念和组件的概述,并显示了使用默认TaskExecutorPartitionHandler在单独的本地执行线程中进行分区的示例。要将远程分区划分到多个 JVM,需要两个附加组件:
远程处理结构或网格环境
PartitionHandler实现支持所需的远程结构或网格环境
与远程分块类似,JMS 可以用作“远程处理结构”。在这种情况下,如上所述,请使用MessageChannelPartitionHandler实例作为PartitionHandler实现。以下示例假定一个现有的分区作业,并着重于MessageChannelPartitionHandler和 JMS 配置:
XML Configuration
<bean id="partitionHandler"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.partition.MessageChannelPartitionHandler">
<property name="stepName" value="step1"/>
<property name="gridSize" value="3"/>
<property name="replyChannel" ref="outbound-replies"/>
<property name="messagingOperations">
<bean class="org.springframework.integration.core.MessagingTemplate">
<property name="defaultChannel" ref="outbound-requests"/>
<property name="receiveTimeout" value="100000"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<int:channel id="outbound-requests"/>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter destination="requestsQueue"
channel="outbound-requests"/>
<int:channel id="inbound-requests"/>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter destination="requestsQueue"
channel="inbound-requests"/>
<bean id="stepExecutionRequestHandler"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.partition.StepExecutionRequestHandler">
<property name="jobExplorer" ref="jobExplorer"/>
<property name="stepLocator" ref="stepLocator"/>
</bean>
<int:service-activator ref="stepExecutionRequestHandler" input-channel="inbound-requests"
output-channel="outbound-staging"/>
<int:channel id="outbound-staging"/>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter destination="stagingQueue"
channel="outbound-staging"/>
<int:channel id="inbound-staging"/>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter destination="stagingQueue"
channel="inbound-staging"/>
<int:aggregator ref="partitionHandler" input-channel="inbound-staging"
output-channel="outbound-replies"/>
<int:channel id="outbound-replies">
<int:queue/>
</int:channel>
<bean id="stepLocator"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.partition.BeanFactoryStepLocator" />
Java Configuration
/*
* Configuration of the master side
*/
@Bean
public PartitionHandler partitionHandler() {
MessageChannelPartitionHandler partitionHandler = new MessageChannelPartitionHandler();
partitionHandler.setStepName("step1");
partitionHandler.setGridSize(3);
partitionHandler.setReplyChannel(outboundReplies());
MessagingTemplate template = new MessagingTemplate();
template.setDefaultChannel(outboundRequests());
template.setReceiveTimeout(100000);
partitionHandler.setMessagingOperations(template);
return partitionHandler;
}
@Bean
public QueueChannel outboundReplies() {
return new QueueChannel();
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel outboundRequests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundJmsRequests() {
return IntegrationFlows.from("outboundRequests")
.handle(Jms.outboundGateway(connectionFactory())
.requestDestination("requestsQueue"))
.get();
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "inboundStaging")
public AggregatorFactoryBean partitioningMessageHandler() throws Exception {
AggregatorFactoryBean aggregatorFactoryBean = new AggregatorFactoryBean();
aggregatorFactoryBean.setProcessorBean(partitionHandler());
aggregatorFactoryBean.setOutputChannel(outboundReplies());
// configure other propeties of the aggregatorFactoryBean
return aggregatorFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel inboundStaging() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow inboundJmsStaging() {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory())
.configureListenerContainer(c -> c.subscriptionDurable(false))
.destination("stagingQueue"))
.channel(inboundStaging())
.get();
}
/*
* Configuration of the worker side
*/
@Bean
public StepExecutionRequestHandler stepExecutionRequestHandler() {
StepExecutionRequestHandler stepExecutionRequestHandler = new StepExecutionRequestHandler();
stepExecutionRequestHandler.setJobExplorer(jobExplorer);
stepExecutionRequestHandler.setStepLocator(stepLocator());
return stepExecutionRequestHandler;
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "inboundRequests", outputChannel = "outboundStaging")
public StepExecutionRequestHandler serviceActivator() throws Exception {
return stepExecutionRequestHandler();
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel inboundRequests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
public IntegrationFlow inboundJmsRequests() {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory())
.configureListenerContainer(c -> c.subscriptionDurable(false))
.destination("requestsQueue"))
.channel(inboundRequests())
.get();
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel outboundStaging() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundJmsStaging() {
return IntegrationFlows.from("outboundStaging")
.handle(Jms.outboundGateway(connectionFactory())
.requestDestination("stagingQueue"))
.get();
}
您还必须确保分区handler属性 Map 到partitionHandler bean,如以下示例所示:
XML Configuration
<job id="personJob">
<step id="step1.master">
<partition partitioner="partitioner" handler="partitionHandler"/>
...
</step>
</job>
Java Configuration
public Job personJob() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("personJob")
.start(stepBuilderFactory.get("step1.master")
.partitioner("step1.worker", partitioner())
.partitionHandler(partitionHandler())
.build())
.build();
}
您可以找到远程分区作业here的完整示例。
@EnableBatchIntegration注解可用于简化远程分区设置。该注解提供了两个可用于远程分区的 bean:
RemoteChunkingMasterStepBuilderFactory:用于配置主步骤RemotePartitioningWorkerStepBuilderFactory:用于配置工作程序步骤
这些 API 负责配置许多组件,如下图所示:
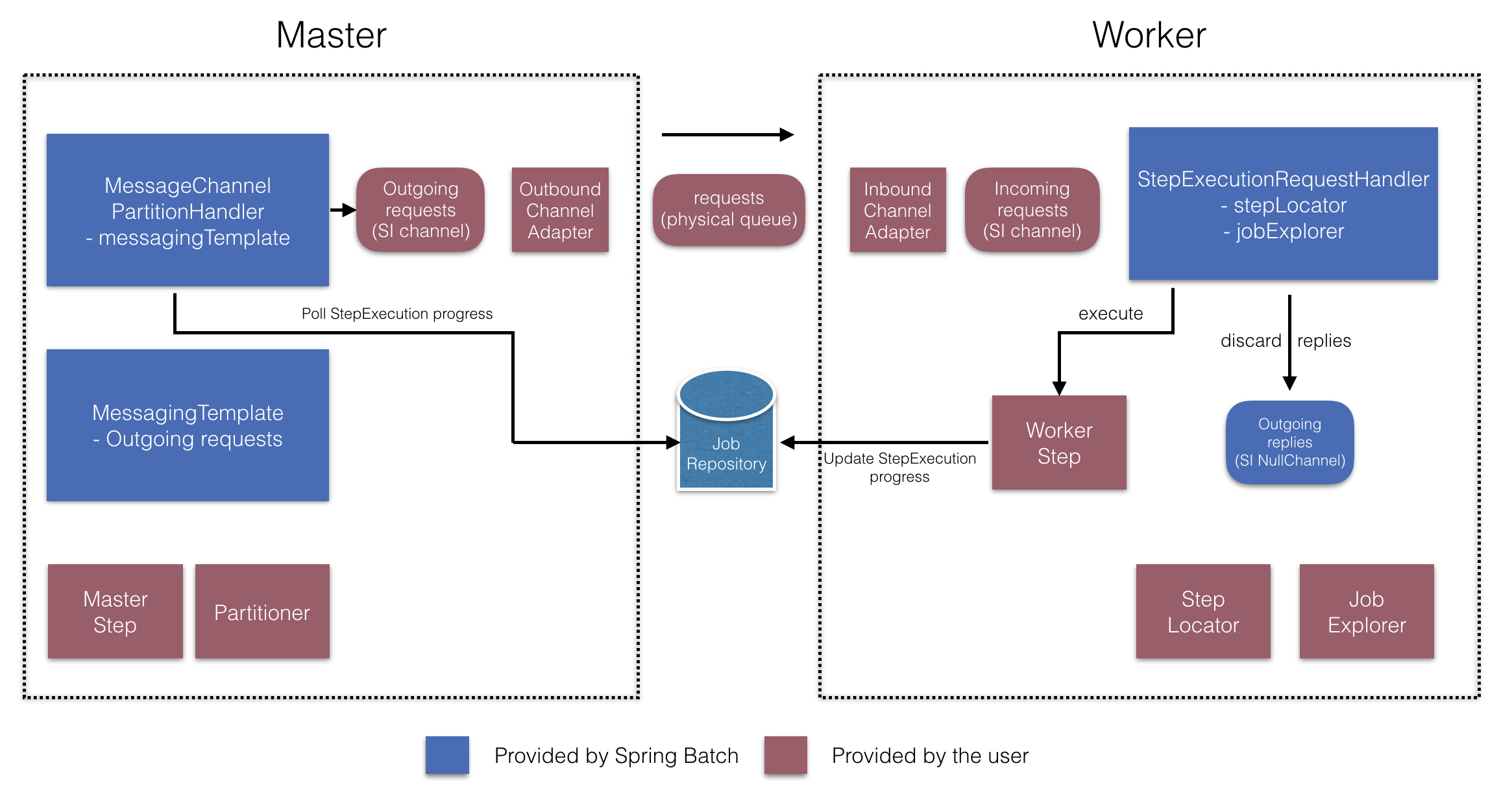
图 6.远程分区配置(带有作业存储库轮询)
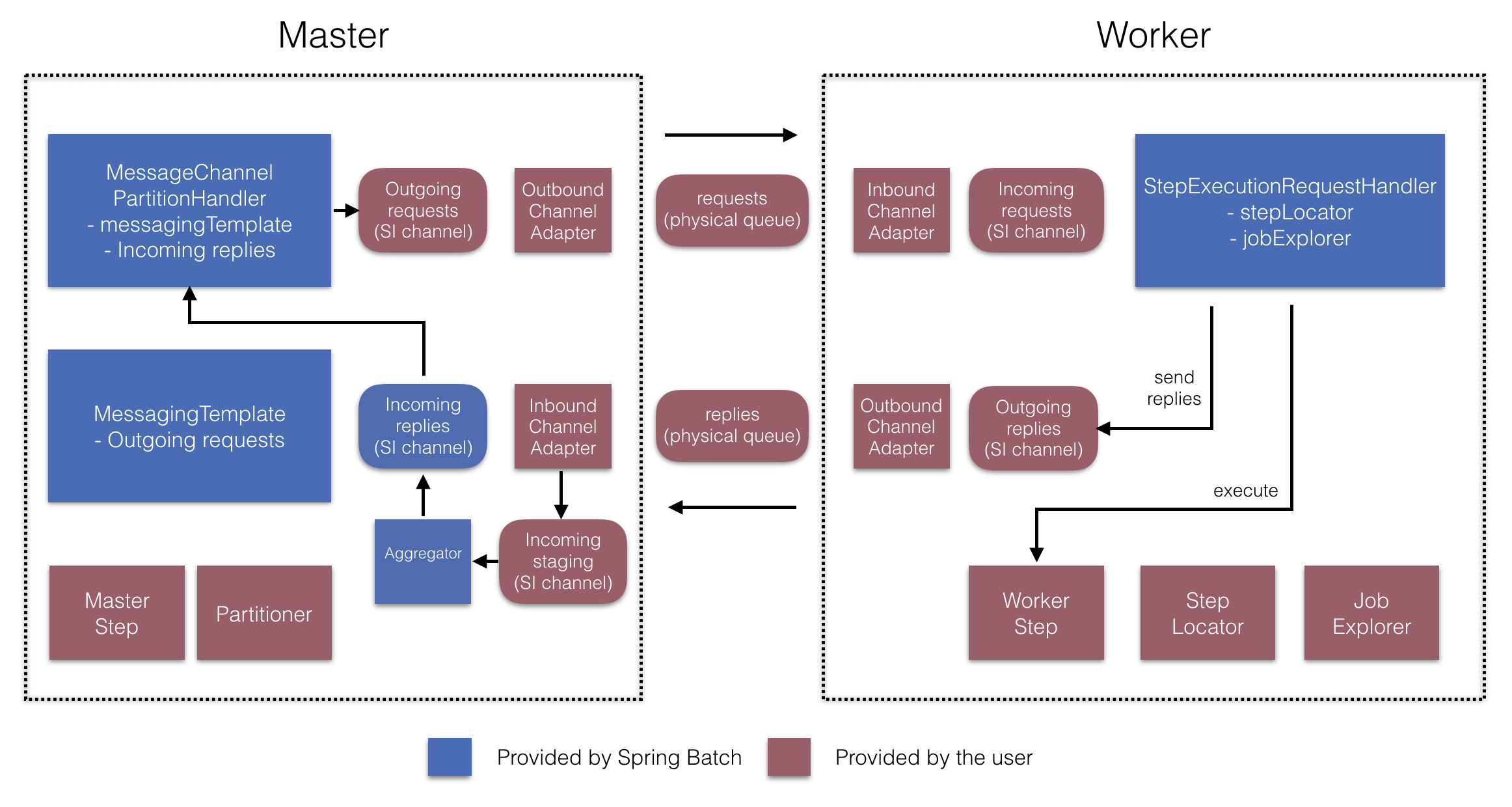
图 7.远程分区配置(带有回复聚合)
在主服务器端,RemoteChunkingMasterStepBuilderFactory允许您pass 语句以下内容来配置主服务器步骤:
Partitioner用于分区数据输出通道(“传出请求”)将请求发送给工作人员
Importing 通道(“传入答复”)以接收工作人员的答复(配置答复聚合时)
轮询间隔和超时参数(在配置作业存储库轮询时)
无需显式配置MessageChannelPartitionHandler和MessagingTemplate(如果需要,仍可以显式配置它们)。
在工作程序端,RemoteChunkingWorkerBuilder允许您将工作程序配置为:
侦听主机在 Importing 通道上发送的请求(“传入请求”)
为每个请求调用
StepExecutionRequestHandler的handle方法将输出通道上的回复(“传出回复”)发送给主服务器
无需显式配置StepExecutionRequestHandler(可以根据需要显式配置)。
以下示例显示了如何使用这些 API:
@Configuration
@EnableBatchProcessing
@EnableBatchIntegration
public class RemotePartitioningJobConfiguration {
@Configuration
public static class MasterConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemotePartitioningMasterStepBuilderFactory masterStepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public Step masterStep() {
return this.masterStepBuilderFactory
.get("masterStep")
.partitioner("workerStep", partitioner())
.gridSize(10)
.outputChannel(outgoingRequestsToWorkers())
.inputChannel(incomingRepliesFromWorkers())
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
@Configuration
public static class WorkerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemotePartitioningWorkerStepBuilderFactory workerStepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public Step workerStep() {
return this.workerStepBuilderFactory
.get("workerStep")
.inputChannel(incomingRequestsFromMaster())
.outputChannel(outgoingRepliesToMaster())
.chunk(100)
.reader(itemReader())
.processor(itemProcessor())
.writer(itemWriter())
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
}